Ever wondered how blockchain powers cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or tracks goods across the globe? You’re scrolling through X, and someone posts about blockchain’s “decentralized magic,” but the tech jargon—nodes, hashes, consensus—leaves you dizzy. If you’re a 30–40-year-old professional, maybe dabbling in tech investments or curious about secure transactions, understanding how blockchain works can feel like cracking a code. This step-by-step guide demystifies the process, with real-world examples and practical insights to make blockchain technology clear. Let’s dive into the mechanics of blockchain and why it’s a game-changer in 2025.
Table of Contents
- What Is Blockchain? A Quick Recap
- How Blockchain Works: Step-by-Step
- Consensus Mechanisms Explained
- Why Blockchain Is Secure
- Real-World Examples of Blockchain in Action
- Challenges in Blockchain Operations
- How Blockchain Processes Evolve in 2025
- FAQs About How Blockchain Works
- Conclusion: Start Exploring Blockchain
What Is Blockchain? A Quick Recap
Blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers, making them secure and transparent. Unlike a bank’s centralized database, blockchain is decentralized—no one controls it, yet everyone in the network can trust it. Each transaction is stored in a “block,” linked to the previous one, forming a tamper-proof chain.
Imagine you’re Lisa, a 35-year-old small business owner. You pay a supplier overseas. Banks take days and charge high fees. Blockchain logs the payment instantly, verifies it globally, and completes it in minutes. That’s the core of blockchain technology explained. For a broader intro, see Blockchain 101.
How Blockchain Works: Step-by-Step
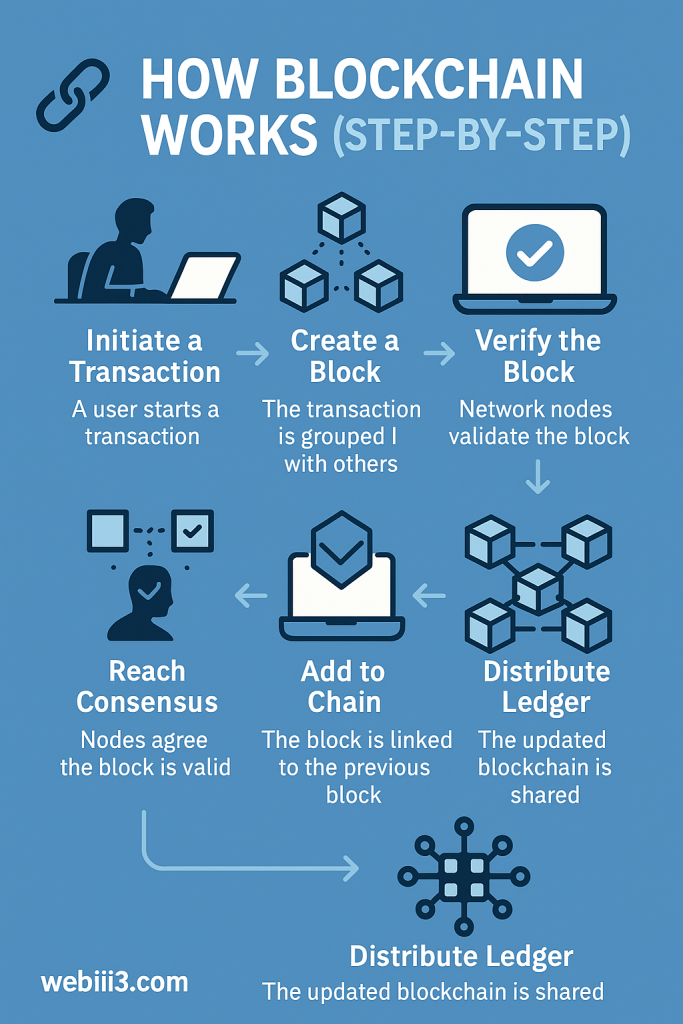
Blockchain’s process is like a well-oiled machine. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Initiate a Transaction: You start an action, like sending $50 in Bitcoin. Where: On a blockchain app (e.g., MetaMask). Time: Seconds. Resource: Crypto wallet.
- Create a Block: Your transaction is bundled with others into a block. Where: Network servers. Time: 1–2 minutes. Resource: Blockchain protocol.
- Verify the Block: Nodes (computers) check the block’s validity using algorithms. Where: Global network. Time: 1–10 minutes. Resource: Computing power.
- Reach Consensus: Nodes agree the block is legit, preventing fraud. Where: Network-wide. Time: Seconds. Resource: Consensus algorithm.
- Add to Chain: The block is linked to the previous one with a cryptographic hash. Where: Blockchain ledger. Time: Instant. Resource: Encryption software.
- Distribute Ledger: The updated chain syncs across all nodes. Where: Every node. Time: Seconds. Resource: Internet connection.
This process, often under 10 minutes, ensures security and transparency. It’s like a global team double-checking your work in real-time.
Consensus Mechanisms Explained
Consensus is how blockchain ensures everyone agrees on the ledger. The two main methods are:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Nodes solve complex puzzles to validate blocks, used by Bitcoin. It’s secure but energy-intensive.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on their crypto holdings, used by Ethereum. It’s faster and eco-friendly.
PoW vs. PoS
| Aspect | Proof of Work | Proof of Stake |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Use | High (mining rigs) | Low (no mining) |
| Speed | Slower (10 min/block) | Faster (seconds/block) |
| Example | Bitcoin | Ethereum 2.0 |
For more, check Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake.
Why Blockchain Is Secure
Blockchain’s security comes from its design. Each block has a unique hash—a digital fingerprint—linking it to the previous block. Changing one block requires altering all subsequent blocks across thousands of nodes, which is computationally impossible. Cryptographic encryption further locks data.
Take Sarah, a 32-year-old nurse. Her hospital uses blockchain to store patient records. Only authorized doctors access them, and any attempt to tamper is flagged instantly. In 2024, blockchain prevented $1.2 billion in fraud, per CoinDesk. It’s like a vault with a million locks.
Real-World Examples of Blockchain in Action
Blockchain’s process shines in real-world scenarios. Here are three examples:
Finance: Fast Payments
Ripple’s blockchain processes cross-border payments in seconds. In 2024, it saved banks $500 million in fees, per Ripple.
Supply Chain: Transparent Tracking
Walmart uses blockchain to trace produce. When spinach was recalled in 2024, they pinpointed the source in seconds, per IBM.
Healthcare: Secure Records
Blockchain secures patient data, cutting hospital admin costs by 15% in 2024, per industry reports.
Challenges in Blockchain Operations
Blockchain isn’t perfect. Here are key hurdles:
- Scalability: High transaction volumes can slow networks. Ethereum’s layer-2 solutions help, but challenges remain.
- Energy Use: PoW consumes massive power, though PoS is greener.
- Complexity: The tech can intimidate beginners.
Still, innovations are tackling these. For more, see Solving Blockchain Scalability. Honestly, it’s exciting to watch this tech evolve.
How Blockchain Processes Evolve in 2025
Blockchain is getting faster and greener. Statista predicts the market will hit $39 billion by 2025, driven by:
- Layer-2 Solutions: Speeding up transactions (e.g., Polygon).
- Green Consensus: PoS adoption cuts energy use by 99% vs. PoW.
- Interoperability: Blockchains like Polkadot connect different networks.
For investors like Mike, a 38-year-old dad, this means more efficient DeFi platforms. It’s like watching the internet mature in the ‘90s—full of potential.
FAQs About How Blockchain Works
How does blockchain work in simple terms?
Blockchain records transactions in blocks, verified by a network of computers, and links them in a secure chain. It’s like a shared, tamper-proof ledger that updates across all nodes.
Why is blockchain considered secure?
Blockchain uses cryptographic encryption and decentralization, making it nearly impossible to alter data without network consensus. Each block is locked with a unique hash.
How long does a blockchain transaction take?
Most blockchain transactions take minutes, depending on the network. For example, Bitcoin averages 10 minutes, while Ethereum can be faster with layer-2 solutions.
What’s the difference between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake?
Proof of Work requires computers to solve complex puzzles to validate transactions, using more energy. Proof of Stake selects validators based on their crypto holdings, being more energy-efficient.
💡 Have questions about blockchain? Leave a comment or subscribe for hands-on tutorials — and stay ahead of Web3 innovation! Visit Web3 Learning Hub to keep learning.
Last updated: April 30, 2025

Pingback: Blockchain 101: A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Blockchain Technology - Web3 Innovations & Future Technologies | webiii3.com