Ever wondered what sets public and private blockchains apart in the buzzing world of decentralized technology? If you’re new to blockchain or deciding which type fits your project in 2025, understanding the differences between public vs private blockchains is crucial. Public blockchains, like Bitcoin, are open to everyone, while private blockchains are restricted, offering more control but less transparency. In this guide, we’ll break down their key differences—security, scalability, and use cases—so you can choose wisely. Let’s dive in and clear up the confusion!
Table of Contents
What Are Public and Private Blockchains?
Let’s start with the basics. A public blockchain is a decentralized network where anyone can join, read, or write data—think of it as an open library. Bitcoin and Ethereum are classic examples, with thousands of nodes worldwide ensuring transparency. On the other hand, a private blockchain is like a members-only club. Only authorized participants can access it, making it ideal for businesses needing privacy.
I remember chatting with a friend who works in fintech last summer. She mentioned how her company switched to a private blockchain for internal audits because they needed to keep sensitive data under wraps. Meanwhile, public blockchains thrive on openness, which is why they’re often tied to decentralized networks like cryptocurrencies. This distinction sets the stage for their differences in security, speed, and applications.
Understanding these blockchain types is the first step to navigating the decentralized world. Want to explore more foundational concepts? Check out our Blockchain 101 guide.
Key Differences: Public vs Private Blockchains
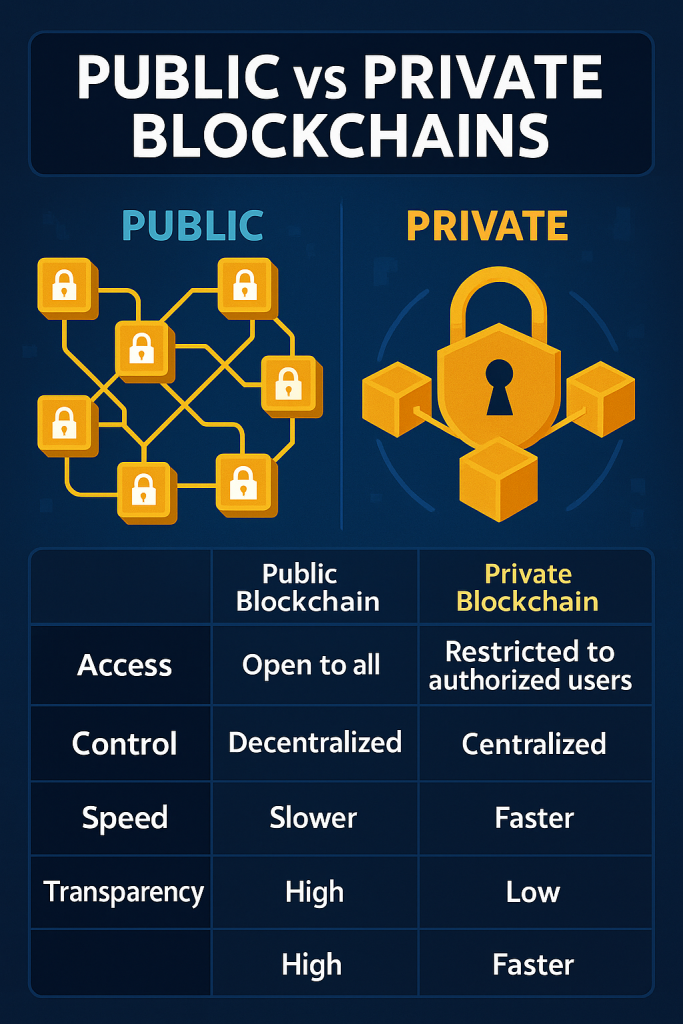
The core differences between public and private blockchains boil down to access, control, and efficiency. Let’s break it down with a comparison table to make things crystal clear.
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Open to all | Restricted to authorized users |
| Control | Decentralized, no single entity | Centralized, managed by an organization |
| Speed | Slower (e.g., Bitcoin: 7 transactions/sec) | Faster (e.g., Hyperledger: 3,000 transactions/sec) |
| Transparency | High, all data is public | Low, data is private |
Public blockchains prioritize transparency over speed, which is why Bitcoin takes about 10 minutes to confirm a transaction. Private blockchains, like Hyperledger Fabric, can process thousands of transactions per second because fewer nodes are involved. This trade-off is something I’ve seen businesses wrestle with—openness versus efficiency.
For more on how blockchains function under the hood, read our step-by-step guide on how blockchain works.
Security in Public and Private Blockchains
Security is a hot topic in the blockchain comparison debate. Public blockchains rely on a vast network of nodes to validate transactions, making them incredibly secure against attacks. For instance, Bitcoin’s network has over 15,000 nodes as of April 2025, according to Bitnodes.io. The more nodes, the harder it is for a malicious actor to take over—think of it as trying to rob a bank with thousands of guards.
Private blockchains, however, have fewer nodes, which can be a double-edged sword. While they’re less vulnerable to external attacks due to restricted access, they’re more susceptible to internal threats. A colleague once shared how a private blockchain they used for supply chain tracking was compromised because an insider leaked access keys—a rare but real risk.
Both types use cryptography, but public blockchains often employ energy-intensive consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work. Curious about consensus mechanisms? Our Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake guide dives deeper.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
Scalability is where private blockchains often shine. Public blockchains like Ethereum struggle with high transaction volumes—Ethereum processes about 30 transactions per second as of 2025, according to Etherscan. This can lead to high fees during peak times, which I’ve experienced firsthand when trying to swap tokens during a crypto bull run last year. Gas fees shot up to $50 for a simple transaction—frustrating, to say the least!
Private blockchains, on the other hand, are built for speed. A private blockchain like Corda can handle up to 1,000 transactions per second, making it ideal for industries like finance. For example, a 2024 report by Deloitte highlighted how a European bank reduced cross-border payment times from 3 days to 10 seconds using a private blockchain.
Scalability solutions are evolving for both types, though. Public blockchains are adopting Layer 2 solutions like rollups, while private blockchains focus on optimizing node efficiency. Learn more about these advancements in our blockchain scalability guide.
Real-World Use Cases: Where They Shine
Public blockchains are the backbone of decentralized applications (dApps). Ethereum, for instance, hosts over 4,000 dApps as of 2025, ranging from DeFi platforms like Uniswap to NFT marketplaces like OpenSea, according to DappRadar. They’re perfect for scenarios where trust and transparency are paramount—like crowdfunding campaigns where donors want to track every penny.
Private blockchains, however, dominate enterprise use cases. IBM’s Food Trust, a private blockchain, tracks food supply chains for companies like Walmart. In 2024, Walmart reported reducing food tracing time from 7 days to 2.2 seconds using this technology—a game-changer for food safety. I recall a grocery store incident where a spinach recall took weeks to trace; private blockchains could’ve saved so much time and worry.
Both types have their place in the decentralized ecosystem. To explore more applications, visit our 2025 blockchain use cases guide.
Which Blockchain Type Should You Choose?
Choosing between public and private blockchains depends on your goals. If you’re building a transparent platform—like a charity dApp where donors need visibility—a public blockchain is the way to go. But if you’re a business handling sensitive data, like a bank managing client transactions, a private blockchain offers the control and speed you need.
Here’s a quick decision guide: Need openness and trust? Go public. Need privacy and efficiency? Go private. Still unsure? Our Web3 Learning Hub has more resources to help you decide.
Both blockchain types are shaping the future of decentralized networks. Bookmark this guide or share it with a friend who’s curious about blockchain technology—it might just spark their next big idea!
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the main difference between public and private blockchains?
Public blockchains are open to everyone, like Bitcoin, while private blockchains restrict access to authorized users, often used by businesses for privacy.
Are public blockchains more secure than private ones?
Public blockchains can be more secure against external attacks due to their large node networks, but private blockchains are safer from internal threats if managed well.
Which blockchain type is faster for transactions?
Private blockchains are generally faster. For example, a private blockchain like Hyperledger can process 3,000 transactions per second, while Bitcoin handles about 7.
Can I use a public blockchain for my business?
Yes, but it depends on your needs. Public blockchains are great for transparency, but if you need privacy for sensitive data, a private blockchain might be better.
Related Articles
Ready to Dive Deeper into Blockchain?
The world of blockchain types is vast and exciting—don’t stop here! Explore more in our Web3 Learning Hub or subscribe to our newsletter for the latest updates. Take the next step in your blockchain journey today!
Last updated: April 30, 2025